Diet and nutrition are fundamental aspects of overall health and play a crucial role in preventing chronic diseases. The foods we eat provide the essential nutrients our bodies need to function optimally, while dietary patterns can influence the risk of developing various health conditions. In this article, we will explore the vital role of diet and nutrition in preventing chronic diseases and promoting long-term health and well-being.
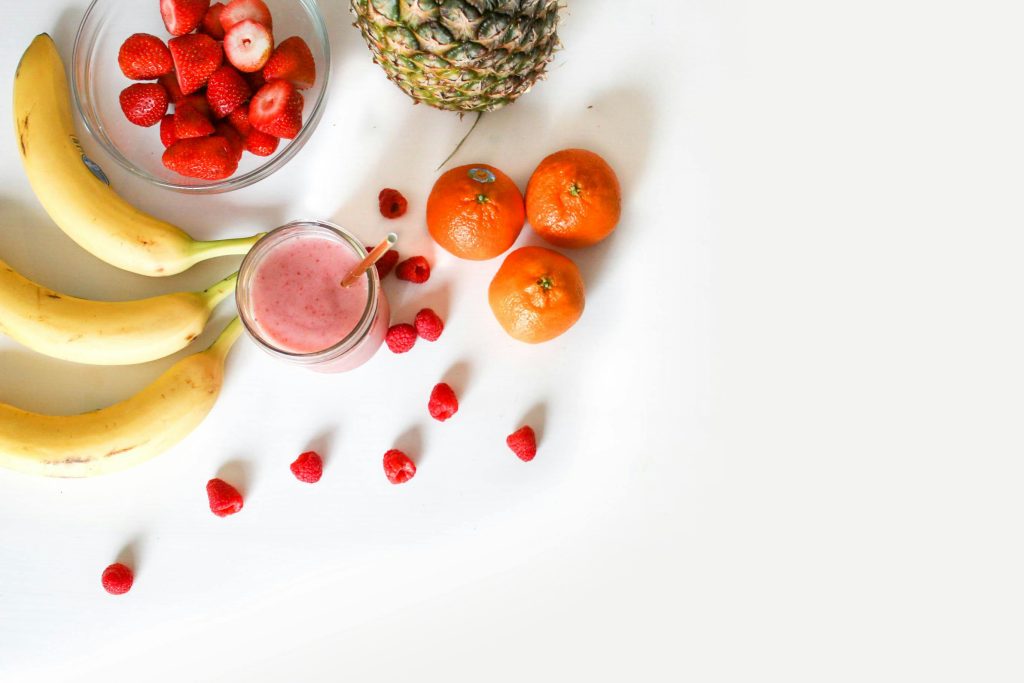

- Balanced Nutrition:
- A balanced diet includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods from all food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Consuming a diverse range of foods ensures adequate intake of essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and immune function.
- Prevention of Obesity and Weight-Related Diseases:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition reduces the risk of obesity-related chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers.
- Choosing nutrient-rich, low-calorie foods and practicing portion control can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Reduction of Cardiovascular Risk Factors:
- A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and triglycerides, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Limiting intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium while increasing consumption of fiber-rich foods promotes cardiovascular health.
- Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes:
- Eating a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, fiber, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Avoiding sugary beverages, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods can help prevent spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels.
- Promotion of Digestive Health:
- A diet high in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics supports digestive health and prevents gastrointestinal disorders such as constipation, diverticulosis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Consuming fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria and improve digestive function.
- Antioxidant Protection Against Chronic Diseases:
- Antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes, help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which can contribute to chronic inflammation and disease.
- Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in the diet provides a wide range of antioxidants with protective effects against chronic diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and age-related macular degeneration.
Diet and nutrition are integral components of preventive healthcare, influencing the risk of developing chronic diseases and promoting overall health and well-being. By adopting a balanced diet that prioritizes nutrient-rich foods and minimizes intake of processed and unhealthy options, individuals can reduce their risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, digestive disorders, and other chronic conditions. Remember, small changes in dietary habits can have a significant impact on long-term health, so prioritize nutrition and make informed choices to support your well-being.